Does the gap between your CTC and take home salary (in-hand salary) confuse you? In this post, you will get a complete guide on how to calculate take home salary from CTC including an excel calculator tool that makes this super easy.
In the February 2020 budget, the option of NEW lower tax rate slabs was introduced where you DON’T get the benefit of any exemptions and deductions. The calculator gives you both the options to choose either the “OLD” regime (with benefit of tax exemptions and deductions) or “NEW ” regime WITHOUT the benefit of exemptions and deductions to arrive at the tax to be deducted from your salary.
If you know the components of your CTC, you can easily calculate your monthly take-home salary from it (the amount you get in your bank account). You can download our excel calculator to do the math for you.
Take Home Salary Calculator India Excel Tool (How to Use)
Just follow the simple steps below to calculate your take home salary from CTC using this excel calculator:
- Step 1 Download our Excel Calculator Tool or use this online version enter your CTC breakup as per the offer letter in the Input Sheet. The calculator is updated for the Financial Year 2023-24
- Step 2 Choose if you want to opt for OLD Tax Slab Scheme (WITH Benefit of tax exemptions and deductions) or NEW Scheme of Taxation (Lower Tax rates WITHOUT benefit of exemptions, deductions).
The general rule of thumb is that the old scheme is more beneficial and this is the default selection.
But you can consider NEW scheme if you don’t claim much tax exemptions under HRA, LTA or deductions like 80C, 80D etc.
With this calculator, you can check your take home salary using both the schemes to see which one gives you a better deal.
- Step 3 Enter details of your estimated House Rent Allowance, Leave Travel Allowance, telephone reimbursement and other claims (more about it here)
- Step 4 Enter details of other income and interest paid on self occupied house property (if any)
- Step 5 Enter details of likely investments in the financial year (under 80C, 80D etc)
Steps 3 to 5 are optional if you choose to opt for NEW SCHEME of Taxation.
Based on these inputs, you will be able to get an estimated calculation of your Take Home Salary.
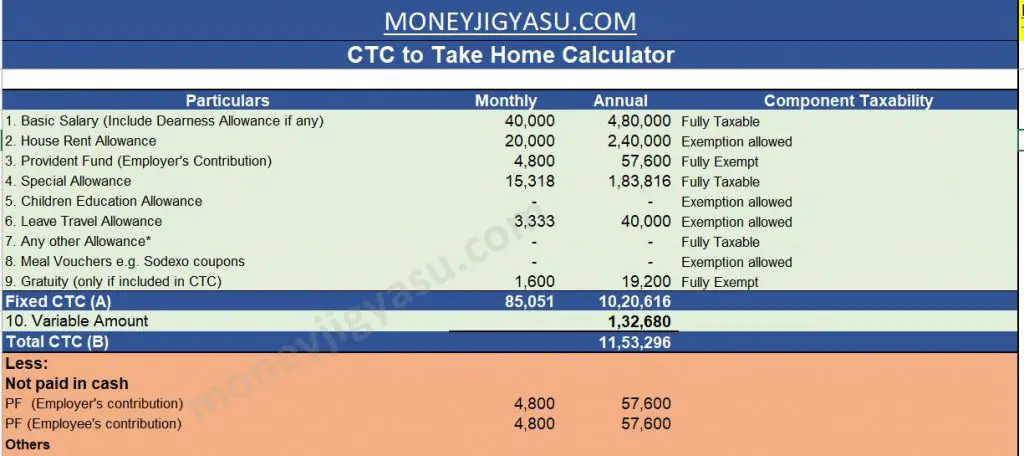
More about Take Home Salary Calculator Tool Excel
Our Take Home Salary Calculator India 2023-24 tool helps you quickly calculate your estimated monthly take home salary from your CTC. It now also provides option to calculate your take home salary choosing either “Old” or “New Tax Slabs” to calculate your estimated tax liability.
This excel file is designed to help you get an idea of what % of CTC you will actually take home.
It gives you an estimate of your take home salary, considering your investments and estimated tax liability.
Terms of usage: The calculator is for reference and educational purpose only and not professional or legal advice for taking decisions. Although care has been taken in making this calculator as accurate as possible, there may be deviations in individual cases and take home figure is only an estimate.
If you have any doubts or queries about using the calculator or your CTC components, please mention in the comments section on our website or shoot a mail to newsletter@moneyjigyasu.com with subject “CTC to take home Calculator-Query”.
Scope of Take Home Salary Calculator India Excel (In-Hand Salary Calculator India)
This calculator works if you have the following elements in your CTC:
1. Basic Salary (Include Dearness Allowance if any)
2. House Rent Allowance
3. Provident Fund (Employer’s Contribution)
4. Conveyance Allowance
5. Medical Allowance
6. Telephone Allowance / Reimbursement (Enter if included in CTC)
7. Leave Travel Allowance
8. Meal Vouchers e.g. Sodexo/Food cards
9. Children Education Allowance
10. Car Running Allowance – Petrol and Driver Salary Reimbursement
11. Special Allowance
12. Any other Allowance* (will be assumed to be taxable)
13. Gratuity (Enter only if included in CTC)
If any of the above components i.e. variable, gratuity etc. is not a part of your CTC, simply enter the amount as “0”
You can get an estimate of the monthly take home salary from CTC once you enter all the details.
Note: This Salary Calculator India tool covers the normal CTC components for private sector employees and may not be suitable for government employees whose CTC structure is quite different.
SURVEY- What percentage of CTC is your take home salary?
Have you calculated your take home salary? Share your insights.
What % of your CTC do you get in hand?
Do you want to get a good understanding of the “why” behind the formula/calculator?
Read further on how different CTC components affect your take home salary.
I have also chipped in some insights on things you need to ask the HR before accepting an offer.
CTC vs Take Home Salary- The Difference
The CTC amount, that your employer mentions in the offer letter is simply how much they will spend on you annually. Not what they are going to pay you.
After all, the very meaning of CTC is “Cost to the Company”.
Think of CTC as the total cake of which a major piece goes to the government in the form of taxes (TDS, which depends a lot on your total income), another cut goes towards your retirement funds (Provident Fund) and only a part of it is actually paid out in cash.
Your Take Home Salary (also called as net salary) is the amount that you will get in your bank account after taxes and all other deductions like Provident Fund, Profession tax, etc.
Unfortunately, most of us realise this only after checking the pay-slip. And then there is heartburn…….

What impacts your take home salary?
Broadly, there are two things that have the biggest impact on your CTC:
- Your CTC structure – What components your CTC has
- Your Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) – What is the tax deducted on your salary considering your tax deductions, exemptions and your tax slabs
Understanding the components of CTC
Why is your CTC structure important?
Simply because not all CTC components are equally taxable or payable every month.
They may not be even payable in cash.
So let’s break down the common CTC components to understand it better. Your CTC will most likely consist of:
- Basic Salary
- Allowances
- Provident Fund
- Gratuity (ideally should not form part of CTC, but some companies include this as well)
- Variable Portion / Performance Compensation (some companies keep this in addition to CTC)
- Perquisites
1. Basic Salary
Impact on take home salary: High, Taxability: Fully Taxable
It is the most critical component of your CTC.
Basic salary is something you are assured of getting in cash.
It is usually 20% to 45% of CTC depending on the total CTC.
Unfortunately, it is also fully taxable. So a higher basic salary does not mean a higher take home.
Your basic salary has a direct impact on many other CTC components i.e. HRA, Provident Fund, Gratuity, LTA as they are usually a percentage of Basic Salary.
2. Allowances
Allowances are paid for a particular expense. Companies usually pay allowances which are eligible for tax deductions.
A. House Rent Allowance (HRA)
Impact on take home salary: High, Taxability: Partially to Fully Exempt
HRA is an allowance paid for your house rent expenses. It is the most popular and common component of your salary structure.
This allowance gives you a tax benefit if you stay in a rented accommodation.
It can be a great tax saver.
Even if you stay with your parents and pay rent to them, you can get this benefit. However, you need to take certain care of limits and procedures in this regard, from a tax perspective.
You can take home a good percentage i.e. even up to 100% of HRA amount, if you are able to take benefit of HRA exemption.
Usually, HRA is kept at 50% of Basic Salary (some employer’s use 40%).
The reason behind this is that the HRA received is partially tax-exempt under Indian Income tax law, subject to a maximum of 2 limits, one of which is 50% of basic salary (if you stay in a metro city i.e. Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata). If you stay in a non-metro, the limit is reduced to 40% of basic salary.
Thus, HRA at 50% is beneficial if you stay in in a metro-city.
B. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
Impact on take home salary: Moderate, Taxability: Partially to Fully Exempt
This allowance gives you a tax benefit on travel expenses incurred by you, while on leave.
There is no statutory limit for LTA, under Indian Income tax law. Usually, companies keep LTA amount equal to one month’s basic salary. But it varies from company to company. Some companies keep a fixed amount between Rs. 25,000/- to Rs. 2 lakh or more, based on the grade.
Your ability to take home LTA will depend on your eligible expenses claimed during the year.
Practice of paying LTA- Companies follow different practices for payment of LTA. Some companies pay it only when you claim it, on producing the relevant bills/receipts of travel. This is LTA-reimbursement which is tax-free.
Other companies follow a practice of paying LTA monthly as a part of the salary, after deducting TDS. TDS at year end is then adjusted basis any LTA claims made.
C. Conveyance Allowance (discontinued from Financial Year 2018-19)
An allowance paid for covering your daily conveyance expenses.
Note: Conveyance Allowance along with medical reimbursement has been discontinued from FY 2018-19, as Income Tax Law no longer permits tax deduction. To compensate, a standard deduction of Rs. 40,000/- is allowed under Income Tax law for all salaried employees.
D. Children Education Allowance and Children Hostel Allowance
Impact on take home salary: Very Low, Taxability: Partially to Fully exempt (if you have children and produce receipts)
You can opt for children education allowance as a part of salary structure, to save tax on your children’s education fees.
While your child’s education cost is ever increasing, the Income Tax Law has not kept pace with it.
You can get a maximum tax free allowance of only Rs. 100/- per month per child (up to max. 2 children) i.e. Rs. 1,200/- per year for one child.
However, there is an opportunity to get a deduction on your children’s tuition fees under section 80C.
If your child is going to a hostel, then you can further opt for tax free children hostel allowance up to a maximum of Rs. 300/- per month per child.
Note: Please note that Children’s Education Allowance is not to be confused with the tax deduction available on your children’s tuition fees under section 80C. While Children Education Allowance does not form part of your taxable salary, Section 80C allows you an opportunity to get it as deduction from your taxable salary.
E. Special Allowances
Impact on take home: High, Taxability: Fully Taxabale
Usually, companies pay the balance CTC amount after considering your mandatory components under special allowance.
This is fully taxable as well.
F. Medical Allowance (discontinued for tax benefit from Financial Year 2018-19)
Medical Allowance also called as medical expenes reimbursement was tax free till FY 2017-18 upto Rs. 15,000/-
It is no longer eligible for tax benefit since the introduction of standard deduction on salary from FY 2018-19.
3. Provident Fund
Impact on take home salary: High, Taxability: Fully Exempt
When you opt for PF, you are basically agreeing with your employer to contribute a part of CTC to your retirement fund i.e. your PF account and not receive the amount in cash. Click here for more details on PF.
In addition, you also agree to contribute an equal amount from your monthly pay.
As a result, this component has a significant impact on your take home salary.
Usually, PF amount is at the rate of 12% on Basic Salary (as per Indian Law).
Since both you and your employer contribute an equal amount, directly to your Provident Fund account, total contribution is 24% of Basic salary.
However, what you see in your CTC offer letter is only the employer’s contribution.
Your own contribution is not a cost to your employer and will be directly deducted from the monthly salary.
So for purpose of calculating take home, deduct twice your PF amount as shown in your CTC letter.
Note: Some people may argue that ultimately you will be receiving PF but we don’t consider this money as take home as its really not something that you can control even if its an investment.
4. Gratuity
Impact on take home salary: Medium, Taxability: Fully Exempt
If gratuity is showing in your CTC letter, ignore it.
Why?
Because you are not even eligible for it, unless you have completed at least five years with your company. (Indian Law: Payment of Gratuity Act)
In fact, it is not even a cost to the company before that. However, companies make an annual provision for this liability, until that time.
5. Variable Salary
Impact on take home salary: Moderate to High, Taxability: Fully Taxable
The variable component which we know by many names including performance compensation, bonus etc.
Your Company pays this amount usually at the end of the year as per your appraisal cycle.
You should find out what appraisal cycle your company follows, before joining.
Also, know when your first appraisal will take place. If your joining date is near the end of the appraisal cycle (say 2- 3 months before), most probably you will not be eligible for immediate appraisal.
In such cases, you will have to wait for more than a year to get the variable part as well as the first hike.
Also, note that the variable compensation is literally “variable,” i.e. you may not be fully paid as per the CTC amount. It often depends on a combination of your individual and Company’s performance.
You should at least get a rough idea of what is the Employer’s practice of paying variable compensation. You can search for this information online on websites like Glassdoor etc. Also, ask your friends, HR etc. for this information.
6. Perquisites
To keep things simple, I have kept perquisites out of this article.
However, have tried to capture a brief summary here for reference:
Many companies offer perquisites like
- Free meals which are entirely tax free. If given as food vouchers, they are exempt upto Rs.100 per meal i.e. say if 2 meals per day x 26 working days (assumed) will be tax free till Rs. 2,600 per month
- Car Lease Charges, Petrol Reimbursement, maintenance expense. Usually offered at management grade. Taxability depends on the use of the car for official / personal purposes
- Company provided residential accommodation
- Employee Stock Options (ESOPs)
- Telephone / Mobile bill reimbursement for official purpose (completely tax-free without any limit under Income Tax Act)
Companies may also provide other benefits like Group Life Insurance and Group Accident Insurance. This benefit is usually in addition to CTC and you enjoy this insurance only in your capacity as an employee of the company i.e. If you leave the company, you lose the benefit of insurance immediately.
[bctt tweet=”Fast Fact: In 2017, Google CEO Sundar Pichai earned an annual salary of whopping Rs. 1258 crore, but his take home was only Rs. 8.58 crore. Confused! He took a major chunk in stocks i.e. ESOPs.” via=”no”]Flexible Compensation Plan / CTC Structure
Nowadays, companies usually give you the flexibility to choose your CTC structure by keeping only the Basic Salary, Provident Fund and Variable Portion mandatory.
You can choose the other components like HRA, LTA, Children Education Allowance etc. up to certain limits.
Some companies even allow you option on Employee Provident Fund.
Companies also offer other elements like National Pension Scheme, Super- Annuation Contribution etc. which are optional.
This gives you an opportunity to save tax, but they may not be a good investment.
2] TDS
Now we are dealing with the more complicated part.
This is more to do with you than your employer.
From FY 2020-21, you also need to decide if you want to opt for OLD or NEW Scheme of Taxations. You get an option of new lower tax rate slabs in NEW regime but you can’t take the benefit of any exemptions and deductions.
If you opt for OLD scheme, your tax liability will depend on the following elements:
a. Tax Exemptions
The part of your salary income which can be exempted from tax based on your claims i.e.
- Standard Deduction under Section 16(ia) (introduced from Financial Year 2018-19)
A standard deduction of Rs.50,000/- (Rs. 40,000/- for Financial Year 2018-19) is deducted from your salary for TDS purpose. This benefit is available to all salaried employees. (Note: This amount was increased from Rs.40,000/- to Rs.50,000/- in Budget 2019 applicable from financial year 2019-20).
- HRA exemption
The eligible amount of tax exemption you can get on your House Rent Allowance based on your rent amount, location of rental accommodation and basic salary.
- LTA exemption
You can get exemption on the LTA for the eligible amount claimed during the financial year.
b. Deductions from your taxable salary
You can get deduction from your taxable salary for the eligible investments / expenses. It includes the following:
- Section 80C- Collection of Investments / Expenses- Maximum Deduction- Rs. 1,50,000/- per year
- Eligible Expenses- LIC premium payment, Children’s tuition Fees, Home Loan Principal Re-payment etc.
- Eligible Investments- Your PF contribution, ELSS, National Saving Certificates, National Pension Scheme etc.
- Section 80D- Mediclaim Premium paid for yourself and family including parents
- For self, spouse and children- Maximum Eligibility- Rs.30,000/- per year
- For parents- Maximum Eligibility- Rs.30,000/- per year (if any one is a senior citizen- Rs.50,000/- per year)
- Section 80E-Education Loan- Interest on education loan for self, spouse and children is allowed as a deduction without any limit.
- Section 80EEB– Interest on Loan Taken for Purchase of Electric Vehicle upto Rs.1.50 lakhs per year (Loan sanction date Apr 1, 2019 to Mar 31, 2023)
- Section 80G-Donations to eligible institutions (Maximum deduction-usually 50% of the donated amount)
Other Major Deduction: If you have a home loan and pay interest on your house property, it can significantly reduce your tax outflow i.e. since you can claim the interest payments as “loss on house property” up to INR 2 lakhs (INR 3.5 lakhs if affordable housing from FY 2018-19) in a year. This can be a big tax saver.
c. Your Tax Slabs
The tax slab that you fall in after considering your exemptions / deductions has a big impact on your tax liability.
Changes in Budget -Applicable from Financial Year 2019-20
- For those who have Net Taxable Income (after deductions under section 80 C, 80D etc.) up to 5 lakh rupees, there will be no income tax liability due to the 100% tax rebate.
E.g. If your Gross Taxable income is 6.5 lakh rupees and you take full 80C deduction of 1.5 lakh rupees, you will have to pay no tax as Net Taxable income does not exceed 5 lakh rupees.
Note: Don’t be confused. This is not a change in income tax slab. There is no additional benefit, if your Net Taxable Income is greater than 5 lakh rupees.
- Yearly standard deduction for salaried individuals has been increased from Rs.40,000 to 50,000. This gives additional tax savings of maximum Rs.3,120 per year (if you are in the highest slab@30%)
- Interest on Home Loan for affordable home (Value upto Rs. 45 lakhs) increased from 2 lakh rupees per year to 3.50 lakh rupees per year (FY 2018-19).
- Interest on Loan Taken for Purchase of Electric vehicle eligible to be deducted up to Rs. 1.50 lakhs per year under section 80EEB.
Tax slabs for Financial Year 2023-24:
OLD REGIME
| Income Tax Slab | Tax Rate as per Old Regime |
| Up to ₹2,50,000* | Nil |
| ₹2,50,001 to ₹5,00,000 | 5% of total income exceeding ₹2,50,000 |
| ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000 | ₹12,500 + 20% of total income exceeding ₹5,00,000 |
| Above ₹10,00,000 | ₹1,12,500 + 30% of total income exceeding ₹10,00,000 |
*For those who have Net Taxable Income (after deductions under section 80 C, 80D etc.) up to 5 lakh rupees, there will be no income tax liability due to the 100% tax rebate.
NEW REGIME
| Income Tax Slab | Tax Rates As Per New Regime |
| ₹0 – ₹2,50,000 | Nil |
| ₹2,50,001 – ₹ 5,00,000 | 5% |
| ₹5,00,001 – ₹ 7,50,000 | ₹12500 + 10% of total income exceeding ₹5,00,000 |
| ₹7,50,001 – ₹ 10,00,000 | ₹37500 + 15% of total income exceeding ₹7,50,000 |
| ₹10,00,001 – ₹12,50,000 | ₹75000 + 20% of total income exceeding ₹10,00,000 |
| ₹12,50,001 – ₹15,00,000 | ₹125000 + 25% of total income exceeding ₹12,50,000 |
| Above ₹ 15,00,000 | ₹187500 + 30% of total income exceeding ₹15,00,000 |
Conclusion
Hope you have found this article useful. Let us know if you have used the Take Home Salary Calculator India Excel tool to get your take home from CTC. In case you have any queries, just put in the comments below.
Also, check the post below to save tax and maximise your take home salary :
How to increase your Take Home Salary India (10 tips to save upto 2.5 lakhs per year)
Other useful calculators:
References:
Hi, I am CA with a passion for personal finance and investing. I use this blog to share helpful money gyan that I have learned the hard way.

Hi,
Very helpful. I have also bookmarked it.
There is one question – What about ESIC. How will it impact the CTC?
Thanks
Ricky
Thanks for your comment. ESIC will work similar to EPF. Employer’s contribution to ESI will be shown as a part of CTC.
For take home salary calculation, both the employer and employee contribution will have to be deducted from CTC.
However, unlike EPF, there is no income tax deduction available under section 80C for employee’s contribution to ESI. But considering ESIC is applicable only for workers with gross wages upto 21,000/- per month, these employees usually do not fall under income tax net if taxable income is up to Rs. 5 lakhs.
Simple yet brilliant way..!!
The “Other income” from the input sheet (Cell C30) in the excel file isn’t updated to the TDS sheet. Please let me know when you’ve fixed this issue.
This has now been updated. Thanks.
Good information and worksheet that i was searching for. Thanks Dev for the efforts.
Wow..I was looking for this tool to get to know more about how much Salary in hand I will get in my upcoming company.This has helped me lot…Super tool and great work …
This is an excellent tool. Properly laid out with detailed calculations and schedules.
One area which I faced issue with – Surcharge. The tool didn’t compute the surcharge for taxable income above 50L